Choosing a WordPress hosting provider for your website is one of the most critical decisions since it can impact your website’s performance. What makes this decision even trickier is the number of factors you need to consider before deciding which hosting provider is a good fit for your website.
In this article, I will take you through all the important factors to help you make an informed decision. But before we begin, let’s understand the essential elements of a good hosting provider.
There are three S’s that combine to make a good hosting provider: Support, Speed, and Security. Since the advent of managed hosting providers, you can add a fourth S, Scalability, which means that you can increase your server resources at any point based on your site’s requirement.
Let’s look at what you need to factor in before you choose the fastest WordPress hosting.
- Your Technical Ability/Awareness
- How Many Pageviews Your Site Gets?
- Understand Different Types of Hosting
- What About Email and Domain Hosting?
1. Your Technical Ability/Awareness
Table of Contents


You should know your level of understanding of web hosting’s technicalities because this will determine whether you need a managed hosting provider or one that runs on cPanel. A managed hosting provider takes care of all your server-related issues such as caching, backups, scaling, and migrations.
Moreover, you must also consider the support level you need because some hosting providers provide 24/7 customer support through live chat and ticketing service. Others offer round-the-clock phone support, which is more helpful for beginner users.
You would also need to research the level of support your hosting provider offers because the support is often limited to server-related issues. If you are someone who would require help with their website as well, you should look for a host that offers WordPress-level support.
2. How Many Pageviews Your Site Gets?


Hosting providers usually put a limit on pageviews and then charge you extra if you max out that limit which is why you need to analyze how many people will be visiting your website monthly.
If you are planning to host a few people on your site, you should look for a host with a lower traffic limit, but if you have, for example, a huge ecommerce store, then traffic limit is not something you would want in your hosting plan.
Furthermore, bandwidth is something that you should consider well as many hosting providers charge you based on the bandwidth you will consume. Bandwidth is also directly proportional to your pageviews, so a low traffic site will consume less bandwidth and vice versa.
3. Understand Different Types of Hosting


This is where users get confused and make the wrong decision because they are not aware of the different types of servers and which ones they should get. Traditionally, hosting providers are broken up into four different tiers: Shared hosting, Dedicated hosting, VPS, and cloud hosting.
As the name suggests, shared hosting is a shared server where several users use the same server for their websites. They share resources such as RAM, storage, bandwidth, and processor, based on their needs, which means your site’s performance depends on how other sites are utilizing those resources.
There are a few limitations to shared hosting, such as not accessing server functionalities, limiting database access, inability to scale either manually or automatically, and much more.


It is suggested that shared hosting is viable if you have a smaller, less complex website with static content. So if you have a small blog with minimal pageviews a month, then shared hosting can be a good fit for you.
Dedicated hosting is when you have the entire server to yourself, the exact opposite of a shared server. When you opt for a dedicated hosting provider, you rent a physical machine that is entirely yours to use, and since no one else has any share of the server resources, it’s pretty expensive as well. However, just like shared hosting, a dedicated server cannot be scaled. You will have to rent another machine to increase your server resources.


Dedicated servers are usually recommended for extremely busy or mission-critical projects where hundreds and thousands of applications are interconnected and get millions of pageviews by the day.
A VPS or a Virtual Private Server is when a physical server is divided into multiple virtual servers. Each has its dedicated resources, which means you have your own allocated RAM, storage space, and bandwidth, much like a dedicated server. You can even customize your VPS by configuring how much RAM or bandwidth you would require.
One major drawback of a VPS is that if the physical server is somehow compromised, all the VPS is based on that server will automatically be compromised, leaving all websites on that VPS affected.
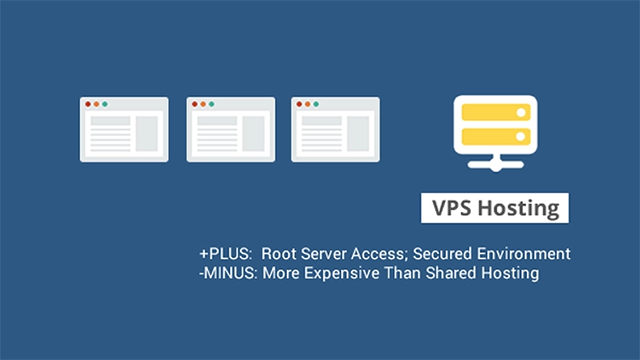

Virtual Private Servers are ideal for people looking to get more control over their server specifications such as RAM and storage and those who have the technical skills to deploy and configure servers.
Cloud hosting has gained massive popularity since its introduction. A cloud server is more or less similar to a VPS, but a key difference is that instead of having a single server, it’s based on several physical machines.
With cloud hosting, you have a network of virtual servers connected together, resulting in higher availability and performance. Cloud hosting is easily scalable, so if you want to increase your server resources, you won’t have to rent another server; you can just scale it up when you need to.
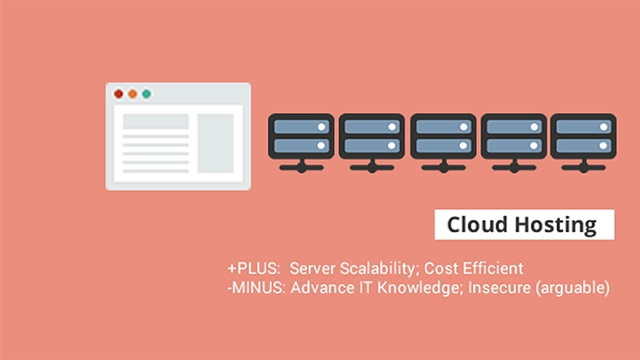

You can find managed cloud hosting solutions where your hosting provider will take care of all your hosting hassles and will provide you with an intuitive platform that you can use to manage your server easily.
4. What About Email and Domain Hosting?


Many hosting providers don’t offer email hosting as part of their stack, which means you will have to find another host for your emails which seems like a hassle, but it’s not. Email hosting doesn’t require much work, you just have to set it and forget it, so if you do have your emails on a separate host, it won’t cost you any extra time.
Similarly, domains can be hosted on a separate host such as Namecheap or GoDaddy without much work. However, there are hosting providers out there who provide domain and email hosting along with application hosting, so if you do want everything under one roof, go with those options.
It is suggested that you keep your domain and email hosting separate because if you decide to migrate to another hosting provider, you will have to move your application and your domain and emails to the new host, which is a huge hassle. Hence, keeping it separate saves you a lot of time and work.
Final Thoughts!
Choosing a hosting provider that matches your requirements can be challenging, so it’s important to consider the factors that I have mentioned in this article. Carefully weigh all the pros and cons of the different types of hosting providers before selecting your desired one.
Author bio: M. Moeez is a WordPress Community Manager at Cloudways. He loves to work closely with customers to understand their problems and come up with solutions that are not only beneficial but are long-lasting as well. He also actively participates in the community to share his knowledge regarding Cloudways and hosting in general. In his free time, he likes to watch football, workout, and spend time on his PlayStation. Get in touch with him at m.moeez@cloudways.com.