Tokyo-based ispace has been selected to deliver rovers from Canada and Japan to the lunar surface after they launch aboard SpaceX rockets. The company will use its recently revealed Hakuto-R lander for both missions, currently scheduled for 2022 and 2023.
The Canadian Space Agency selected three private Canadian companies, each with separate scientific missions, to ride the lander. Mission Control Space Services, Canadensys and NGC are the first companies to receive awards under the CSA’s Capability Demonstration program, part of the agency’s Lunar Exploration Accelerator Program. LEAP, unveiled by the Canadian government in February 2020, earmarks $150 million over five years to support in-space demonstrations and science missions from Canadian private industry.
As part of the mission, the ispace lander will deliver the United Arab Emirates’ The Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC)’s 22 pound rover, “Rashid.” The rover will be equipped with an artificial intelligence flight computer from space robotics company Mission Control Space Services. Mission Control’s AI will use deep-learning algorithms to recognize lunar geology as the Rashid rover traverses the surface.
ispace will carry cameras “to capture key events during the mission” for Canadensys. The Japanese company will also collect lunar imagery data for demonstration of NGC’s autonomous navigation system.
“We are honored that all three of the companies awarded by CSA have each entrusted ispace’s services to carry out their operations on the lunar surface,” ispace founder and CEO Takeshi Hakamada said in a statement. “We see this as a show of the trust that ispace has developed with CSA over the past years, as well as a recognition of ispace’s positive position in the North American market.”
ispace will also be transporting a transformable lunar robot payload to the moon for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), in addition to conducting operations and providing lunar data. The data collected on this mission, Mission 2, will be used to aid the design of a future crewed pressurized rover.
JAXA’s lunar robot will be only around 80mm in diameter before it transforms to its surface form, and will weigh only around 250 grams. That mission is scheduled to take place in 2023. ispace did not disclosed the financial terms of the deals.
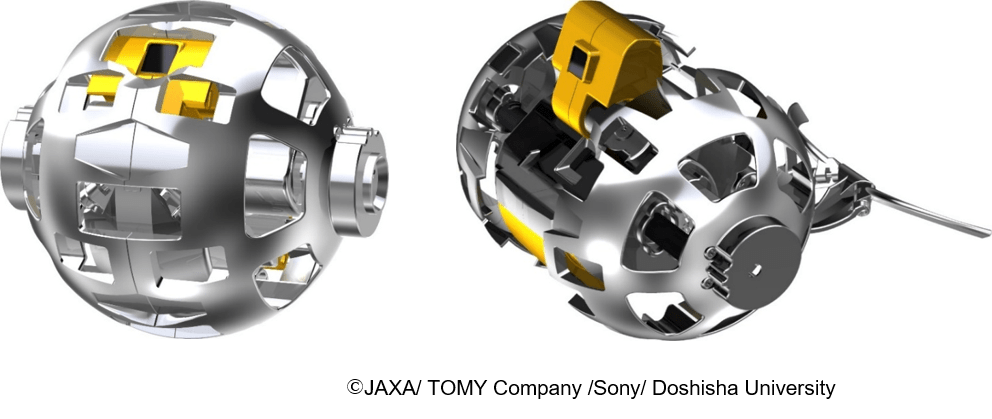
Image Credits: JAXA (opens in a new window)
“While the robot travels on the lunar surface, images on behavior of the regolith, and images of lunar surface taken by the robot and the camera on the lunar lander will be sent to the mission control center via the lunar lander,” JAXA said in a news release. “The acquired data will be used for evaluation of the localization algorithm and the impact of the regolith on driving performance of the crewed pressurized rover.”
ispace unveiled their Hakuto-R lander design in July 2020. The Hakuto project was born out of the Google Lunar XPRIZE competition, in which teams competed to be the first to send a lunar rover to the moon, have it travel 500 meters and send back to Earth photos and video. None of the five finalists, including Hakuto, were able to complete a launch, and the competition subsequently ended in 2018 without a winner.
The MBRSC and JAXA rovers will have different deployment mechanisms from the landers, though Hakamada did not provide further details during a media briefing Wednesday.
The landers are being assembled in Germany and the assembly phase has just started, Hakamada said. “So we’re very confident we will meet this schedule,” he added.
Using water on the lunar surface is one of ispace’s long-term objectives. The company hopes to have more capability in the future to sustain resource utilization activites, Hakamada said.
This is only one of several lunar missions launching on SpaceX rockets. NASA announced in April that the space startup was selected to send humans to the lunar surface as part of its Artemis project, at a total award value of $2.89 billion. SpaceX will also be taking payloads from Firefly Aerosapce to take up its lunar lander in 2023.