The COVID-19 pandemic brought big changes to the healthcare space, and to serve patients in the new environment, providers must have their IT stacks in order.
Learn more about three technology trends healthcare organizations need to stay ahead of to continue to meet patient expectations.
getty
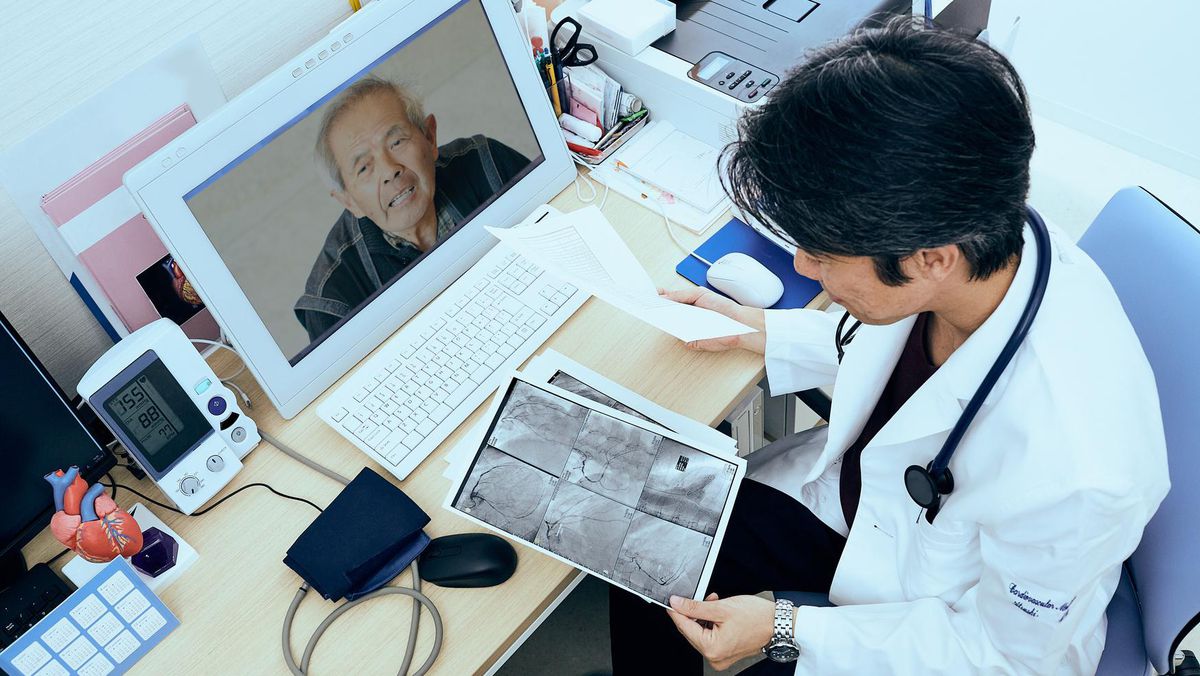
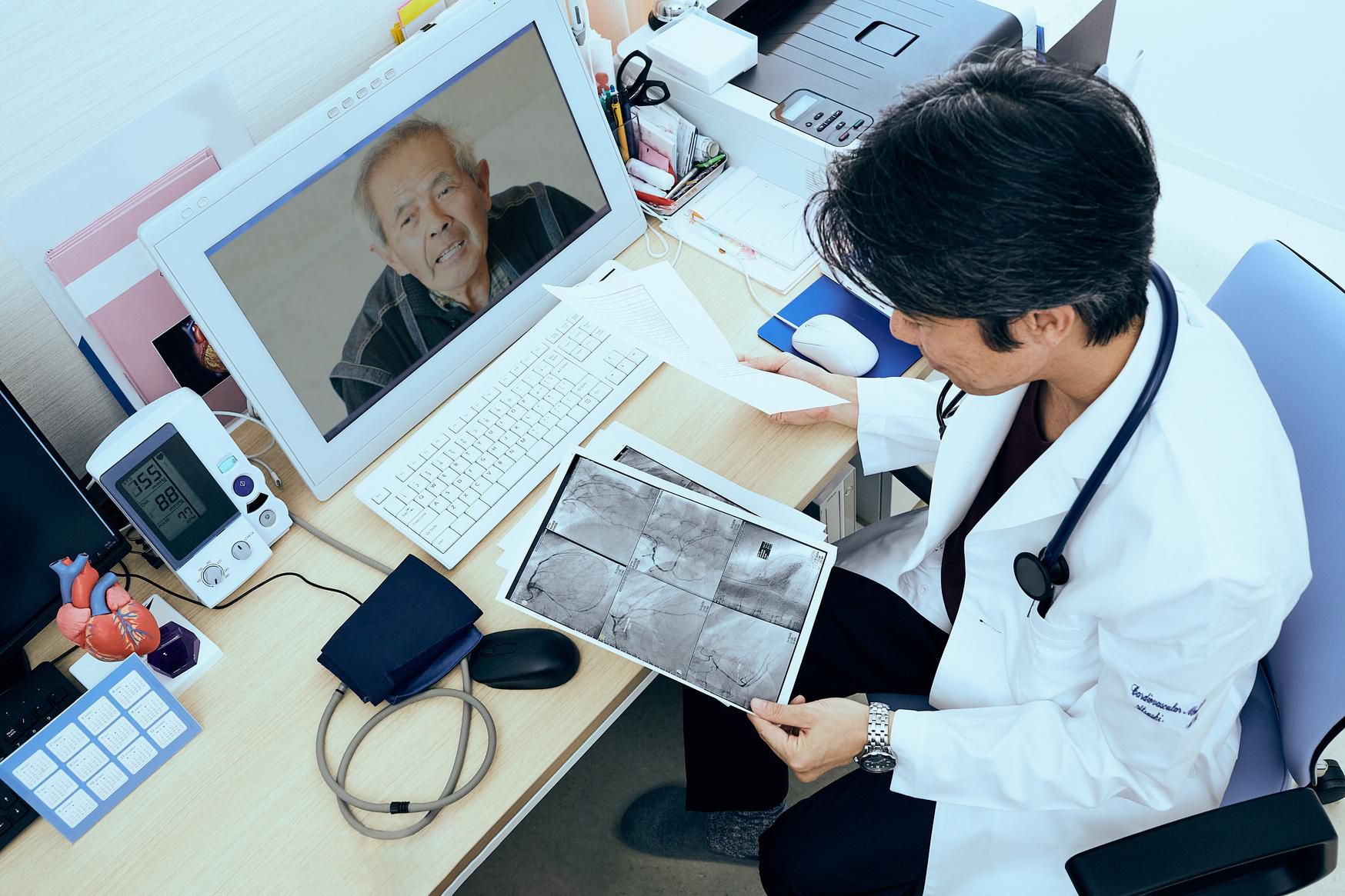
For many kinds of healthcare appointments, virtual care has been the status quo throughout the COVID-19 pandemic—and it is poised to become a lasting, necessary part of the care continuum going forward.
But it’s not enough to offer virtual visits to patients. Healthcare organizations are facing increased pressure from drugstores and other competitors outside of typical healthcare channels. And brand loyalty isn’t guaranteed in a world with lots of options. One recent study from KPMG found that 64 percent of Gen Xers would switch providers just for the convenience of booking appointments online.
With vaccines continuing to roll out, society is evolving toward the “new normal” of post-pandemic life—and to be relevant in that landscape—healthcare organizations need to stay ahead of what patients want. This requires understanding three technology trends affecting patient expectations around healthcare—as well as the IT adjustments that are necessary to put these trends into action.
Trend #1: Virtual care is part of a bigger change toward serving patients in their daily lives.
Table of Contents
As both patients and practitioners embraced previously discouraged or inaccessible communication channels to facilitate appointments during the pandemic, they discovered that virtual care offers better, more convenient access in many circumstances. Virtual care makes it easier for doctors to serve patients when and where they need, including greater opportunity for same-day appointments and greater flexibility after hours or on weekends. According to Amwell’s annual Physician and Consumer Survey, both doctors and patients expect to use telehealth more often; the survey notes that prior to COVID-19, on-demand urgent care was the most common telehealth use case, but that virtual appointments are now embraced across all specialties.
Going forward: Cloud-based infrastructure is the foundation.
Upgrading your infrastructure to handle virtual visits at an enterprise-level scale should be top of mind. Telehealth systems that are easy to adapt and scale will be the most effective line of defense against keeping up with demand. Inflexible systems that can’t adjust to spikes in virtual visits or implement new integrations quickly will severely limit the ability of providers to offer more innovative solutions as virtual care use cases and workflows continue to expand over time. In addition, cloud systems leverage security investments made by hyperscalers, while on-premises security is extremely costly and hard to achieve.
Trend #2: Healthcare data sources have multiplied exponentially.
Companies like Google-owned Fitbit, Apple, Garmin, and Oura are designing wearables equipped with sensors that collect and transmit various health metrics that are becoming increasingly useful for diagnosing medical issues and generating actionable health insights. Paving the way for an expanded Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), these devices (and associated services) are doing things like assessing heart rhythms to detect signs of atrial fibrillation (AFib), measuring respiratory rates using smartphone cameras, and monitoring COPD patients.
Going forward: Big data and analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) based systems will turn data to insights.
The last decade built the devices and user adoption to make mainstream IoMT possible—but now providers must make this foundation useful to patients by turning data into actionable health information. Data must be managed, processed, and analyzed to yield any insights that can improve care and patient outcomes. You will need the proper data management technology, such as a data warehouse, to efficiently consolidate and analyze data from a multitude of data sources. In addition, you will also need to provide sophisticated analytics and BI tools that make it easy for doctors and clinicians to explore, analyze, and share data.
Implementing AI technologies, such as machine learning, will play a critical role in any virtual care strategy. AI-based systems provide speed, efficiency, and precision that can achieve far more than human work alone. For example, AI systems can parse large datasets of similar cases to increase the scope of patient care and treatment. They can also be used to train models for everything from diagnosing serious diseases to protein structure prediction to triaging patient calls.
Trend #3: Treatments and medical collaborations are increasingly taking place on the road.
As medical services are becoming less tethered to specific facilities, healthcare organizations are reimagining how, when, and where care can be delivered. Perhaps one of the most intriguing use cases is improving rapid-response treatment with smart ambulances, which act as both transportation to the hospital and a remote consultation room, complete with live video feeds and virtually-present doctors. The NHS already has plans to roll out a smart ambulance service across the UK, following a trial with the NHS East of England that was particularly successful for stroke treatment.
Going forward: 5G and edge computing will keep services connected, and stringent data security and privacy protection will be mandatory.
The same technologies that let a doctor consult with a patient 100 miles away can assist the same doctor to diagnose ailments around the world. As mobile devices and infrastructure become smarter, anywhere can be the site of sophisticated medical aid during an emergency.
New technologies like 5G and edge computing are helping make the IoMT a reality, enabling connected devices, such as wearables or remote AI-powered tools, to process data closer to where it’s created. 5G also makes it easier for more people to access routine care using virtual care applications, allowing them to connect over video for appointments and other forms of treatment.
During 2020, some regulatory measures were relaxed to make it easier to quickly get virtual care services off the ground. But as patient expectations and needs continue to evolve, and as temporary measures are rolled back post-COVID, you will need to take steps to ensure you can provide virtual care services without compromising personal patient information.
During 2020, some regulatory measures were relaxed to make it easier to quickly get virtual care services off the ground. But as patient expectations and needs continue to evolve, and as temporary measures are rolled back post-COVID, you will need to take steps to ensure you can provide virtual care services without compromising personal patient information. This will include providing secure storage, ensuring limited access to data, using the latest data encryption technology, and implementing a broad range of other security measures, including those that give patients control over and transparency into if and how their data is used.
Get your tech house in order
The trends discussed in this article will endure into post-COVID life, and many more trends will emerge as society transitions. With regulatory and reimbursement requirements currently relaxed, now is the time to take steps toward launching virtual care programs—and that means making sure your technology stack is ready for whatever comes next to serve patients and stay ahead of competitors.
Read this next: See how healthcare execs are tackling transformation. Get the virtual healthcare 2021 report.