A good UX design ensures that your users have an all-around positive experience on your website.
You need a good user experience design:
- If you want to retain your customers in the long term;
- If you want to optimize your product for a specific target group;
- If you want to stand out from the competition with a good user experience.
Implementing a decent UX must take into account business and communication goals while supporting online marketing. The better company goals are brought into line with user expectations, the greater the satisfaction and thus the greater the user’s trust. All of this can be achieved with the help of experience maps. They can help you to:
- Identify the actions taken by the user, thanks to the perfect structuring of the UX mapping data.
- Foster creativity and the invention of new design proposals, which will be tested in the following steps.
- Strengthen synergy and collaboration between members of the UX team, while sharing information, thus providing a better understanding of the user’s profile.
What You Need to Know About User Experience Mapping
Table of Contents
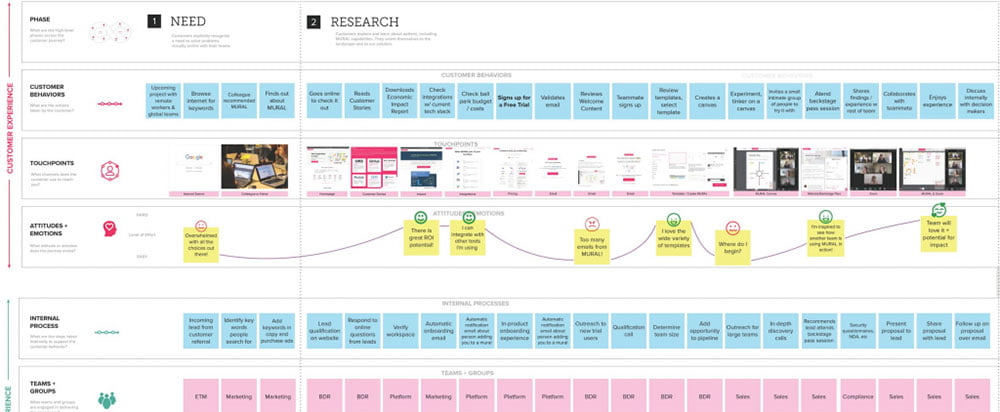
Experience mapping (or UX mapping) designates a graphic and chronological diagram of user behavior during the product/service experience from the first contact, until the sale.
The experience map is a more generic approach than the customer journey mapping, since it addresses different types of products and services, unlike the customer journey map which focuses on a single specific product.
Such a map makes it possible to understand user behavior by illustrating their emotions, reactions, and actions in the form of graphic representations.
These representations provide a summary of the evolution of the user experience by describing its state at each point of contact with the product or service.
In addition, this graphic representation constitutes a practical communication tool that offers members of the UX team an explicit description of the user’s journey. This allows them to have a clearer idea of the behavior of the future user.
In other words, such maps provide you the opportunity to better position yourself in the place of the future user and imagine the different emotions and actions that the latter may express during an interaction with a product/service.
The Difference Between UI and UX
Another term that is often used in connection with user experience design is user interface design. Even if both sub-areas work closely together, the two areas differ in detail more than you might initially think. In general, the main difference is that user experience design looks after the entire process, while user interface design takes care of the individual components.
UX is not the same as UI – even if both topics pursue the same goal: to make user behavior better, simpler, and more intuitive. Remember that a product can work with a bad user interface, but not with a bad user experience. Nevertheless, ideally, the interface and user experience should be coordinated with one another.
What Added Value Does User Experience Have
UX designers often find it difficult to get the rest of the company excited about user experience. Many decision-makers put the technical aspects of a product in the foreground and neglect the user perspective. Others see UX design as an optional step in product development or as an abstract concept that offers no concrete added value.
All of these are misjudgments. UX is neither superfluous nor optional. Companies that neglect ease of use create a serious competitive disadvantage. Nowadays, user experience is an important decision criterion, which in many cases even dwarfs the technical specifications of a product. For example, very few customers are interested in the engine size or acceleration of a car. The driving experience is decisive. The same applies to all other technical products.
It also happens that companies recognize the relevance of UX, but neglect it because it is not directly reflected in metrics. That is also suboptimal. The user experience of an application or a process has a direct influence on a company’s KPIs. These include:
Essentials Steps for Creating a UX Map
Experience maps retrace all the interactions of the user with the product/service and the path he/she must follow to achieve a determined objective. These interactions constitute the user journey. In order to have an overview of these interactions, the following steps must be taken:
The Exploration Phase
In this phase, you have to define the target user flow, based on real data from interviews, surveys, and field studies. Such data is necessary for the creation of personas.
The persona is an archetype or typical model of a potential user. This profile facilitates the identification of the needs of future users and strengthens the understanding of their behavior and state of mind.
Typical user modeling helps the UX designer identify the best optimization options, including navigation and prioritization of content in a website, to improve the user journey and ensure an experience that aligns with its needs.
Define the Stages of the User Journey
This phase consists of listing all the stages that make up the user journey, from the user’s search for the product/service to the purchase, and extends to after-sales service if there is one. This helps determine all the interactions that will be performed during the product experience.
Analysis of the User’s State of Mind
During this stage, the UX design team is focused on studying the subjective aspects of user behavior, namely:
- Their motivations and expectations of the product;
- What they do to achieve a certain goal;
- Their thoughts about each interaction performed;
- Their feelings at each stage of the journey: either satisfied or dissatisfied.
List Interactions With the Product
At this point, the UX team uses graphical representations of the UX display to take an inventory of all the actions the user takes to interact with the product and lists all the touchpoints.
During the user journey, you have to understand what the user thinks and feels. This is when you need to conduct quantitative data analysis to evaluate the evolution of the experience over time and to be able to identify the points of contact required.
Determine Opportunities for Improvement
The compilation of the previous steps reveals the possible pain points that hinder the user from interacting with the product. This relates to the feelings of disappointment and frustration that the user may experience during their UX.
Also, the summaries resulting from the previous steps highlight the significant events or moments of truth from which the user must take decisive action in his journey.
All of this fosters the generation of new opportunities for improvement which helps the UX design team to be more creative and come up with better designs. This ensures the creation of a powerful product, which perfectly meets the expectations of the user.
When is Experience Mapping Clearly the Best Choice
The company chooses the type of mapping to use according to its strategic objectives:
- The “Current State” format. Here, mapping is used as part of the study of the current state of user interaction with the product. It highlights the problems encountered by the latter and the various solutions to overcome them.
- The “Future State” format makes it possible to anticipate the user’s future interactions with a product/service that has not yet been developed. It is always based on real data.
- The “Blueprint” format analyzes the current functioning of the product/service and reveals the details hidden in the user journey.
Final Thoughts
Experience mapping allows the company to refine its design strategies, with the aim of creating a user-centered product/service that meets their expectations. It is a great communication tool that can help to build a shared knowledge between the members of the UX design team, concerning the needs, behavior, and profile of future users.






