In this article, we’ll look at what cloud computing is, the different types of cloud computing, what a cloud provider is, and why you might want to use one. We’ll also survey the best cloud providers, and dig into AWS services in particular and what cloud certification is all about.
Getting Started with Cloud Computing
Table of Contents
When starting your cloud computing career, one of the first steps is to choose a cloud provider. Using that cloud provider’s services, you’ll be able to learn about various cloud computing concepts and get to practice your skills .
What is a cloud provider?
A cloud provider is a company that offers you computing services over the Internet. In the simplest terms, it allows you to store and run your applications on somebody else’s computers.
In reality, you can do more than this with a cloud provider, and you’ll get a glimpse of that in this article!
Why use a cloud provider?
Rather than purchasing equipment, setting up your infrastructure, and maintaining it, you can use a cloud provider.
This way, you can focus on building and maintaining your applications without worrying about the physical infrastructure.
What Cloud Provider to Use?
There are many cloud providers available, and there’s no right or wrong answer when choosing one. Some of the most popular cloud service providers are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
- IBM
- Oracle
Amazon Web Services is the biggest and most popular cloud provider. Another strong point of AWS is its certification program. Amazon’s certifications are among the highest-paying certifications in IT.
As a result, this article focuses on AWS for your introduction to cloud computing. The AWS Cloud Practitioner Certificate is Amazon’s foundational course, which teaches the fundamentals of cloud computing and AWS.
AWS Certifications
Amazon Web Services offers 11 certifications that are divided into four categories.
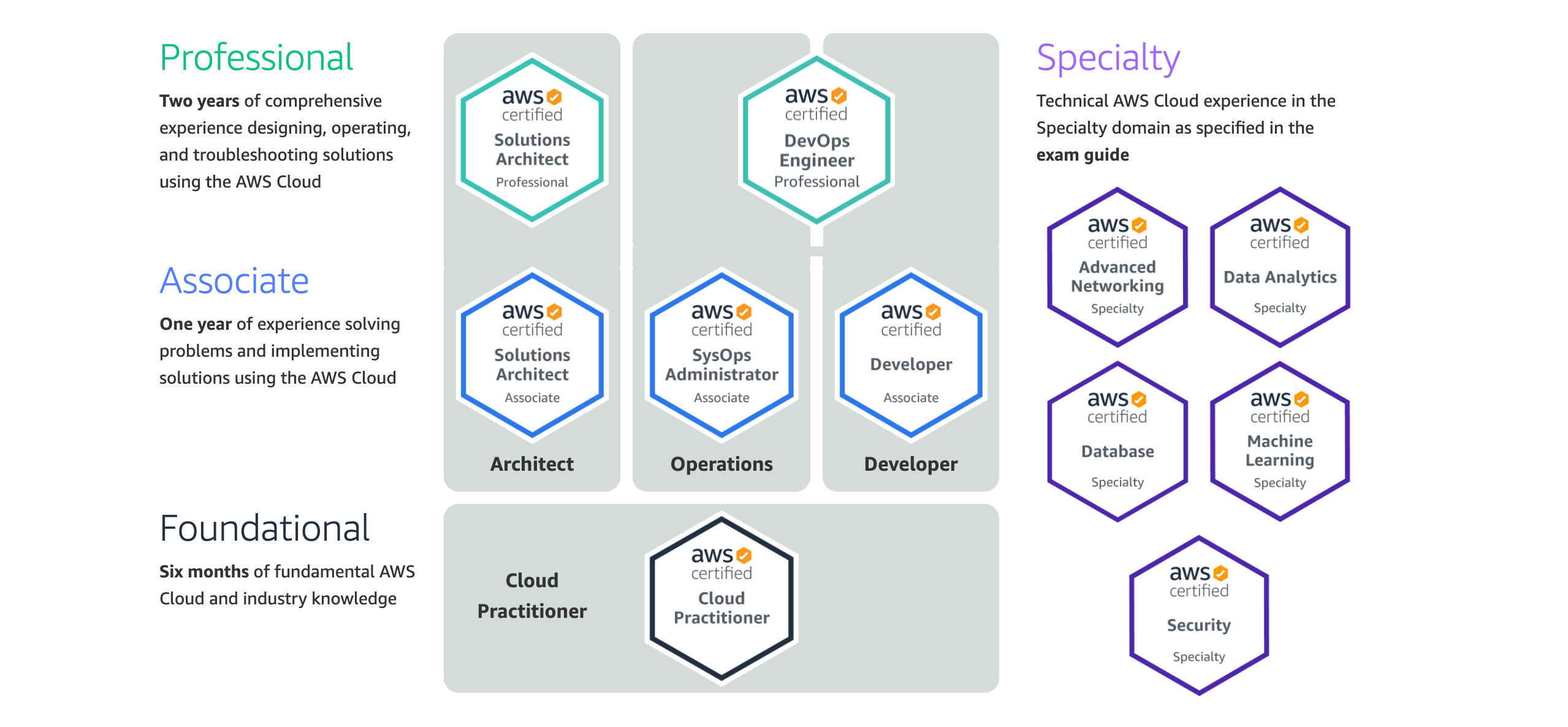
AWS certifications
The Foundational Level has only one certification, the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner certificate. It covers topics such as:
- the fundamentals of cloud computing
- basic AWS information
- the key AWS services
- billing and pricing
- security
The Cloud Practitioner certificate is suitable and recommended for people who are getting started with cloud computing and AWS. To ease you into the cloud world, this article goes over cloud computing and AWS fundamentals. You can use it as a pre-requisite for the Cloud Practitioner certificate.
The next level is the Associate Level, which has three certifications:
- Solutions Architect
- SysOps Administrator
- Developer Associate
These certifications are more complex than the foundational level, and they teach you how to implement solutions using the AWS infrastructure. With the “Associate Level” certificates, you deep dive into services rather than getting an overview of them.
The certificate you choose depends on the path you want to follow. The AWS Solutions Architect certificate helps you gain general AWS expertise. Since it enables you to gain general AWS expertise, you can use it as the foundation for your following certificates.
After the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner certificate, you could work towards the Solutions Architect one.
The following levels, Professional Level and Specialty, are the most difficult certifications. You don’t have to worry about them for now.
What Cloud Computing Is
Let’s start with some fundamental information on cloud concepts. The first question you might ask yourself is “what is cloud computing?”
In layman’s terms, cloud computing is simply like using someone else’s computer. Instead of having your servers, you rent the servers from someone like AWS.
In more sophisticated terms, cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
The Benefits of Cloud Computing
When it comes to cloud computing, there are six significant benefits:
- Variable expense versus capital expense. This means you only pay when you use resources, unlike on-premise resources, where you need to invest a hefty sum beforehand.
- No capacity guessing. You avoid under-utilization or over-utilization of resources. That means you don’t have to pay for underutilized resources, or have your applications down from over-utilized resources. Cloud computing enables you to rapidly scale up or down in response to changing business needs.
- Increased speed and agility. Cloud computing allows you to create or terminate resources within minutes. You don’t have to wait for your IT team for weeks to implement on-premise solutions.
- Benefit from massive economies of scale. You’re splitting the cost with other customers to receive significant discounts.
- Go global. Deploy your applications to various locations worldwide with minimal effort.
- Spending money on running and maintaining data centers. Avoid the headaches, costs, time, and other resources associated with infrastructure development. Let others handle it and focus on your applications.
Now you know what cloud computing is and its six significant benefits. The next stage is to become familiar with the various types of cloud computing.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are three types of Cloud Computing:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service – for admins). You are responsible for managing your servers (either physical or virtual).
- PaaS (Platform as a Service – for developers). There’s no need for you to manage the underlying architecture. You’re only concerned with deploying and running your applications. An example would be Heroku (where you deploy and run web applications).
- SaaS (Software as a Service – for customers). This is a final product that the service provider runs and manages. Google’s Gmail is one example. You don’t have to worry about anything other than using the service.
Cloud Computing Deployments
In addition to the three cloud computing services, there are four cloud computing deployments. These are:
- Public: fully utilizing cloud computing. Examples are AWS, GCP, Azure, IBM, Alibaba, and so on.
- Hybrid: using a mix of public and private deployments. Sensitive and critical information might be stored in a “private” cloud, whereas other information is stored on the “public” cloud.
- Private: deploying resources on-premise and using virtualization and resource management tools.
- Multi-Cloud: a multi-cloud architecture uses various cloud service providers. For instance, you could use a mix of AWS and Google Cloud.
AWS Infrastructure
At the time of writing, Amazon has 81+ availability zones within 25+ geographic regions. There are over 230+ points of presence, split as follows:
- 218+ edge locations
- 12+ regional edge caches
A region is a geographic area, and it consists of at least two availability zones (AZs). The reason for having at least two AZs is in case one of the data centers goes down. For example, one region is eu-west-1 (Ireland). Every region is independent of each other, and the US-EAST is the largest region. As a result, almost all services become available first in this region.
An availability zone is a data center (a building containing lots of physical servers). An availability zone might consist of several data centers, but they’re counted as one AZ because they’re close to each other.
Points of presence are data centers placed at the edge of the networks.
An edge location is an AWS endpoint for caching content. That’s typically CloudFront, which is AWS’s content delivery network. The purpose of these edge locations is to provide low latency for the end users.
There’s a unique region that’s not available to everyone. This region is called GovCloud, and it’s only accessible to companies from the US and US citizens. You also have to pass a screening process. GovCloud allows users to host sensitive Controlled Unclassified Information such as military information.
Continue reading An Introduction to Cloud Computing and AWS Certification on SitePoint.