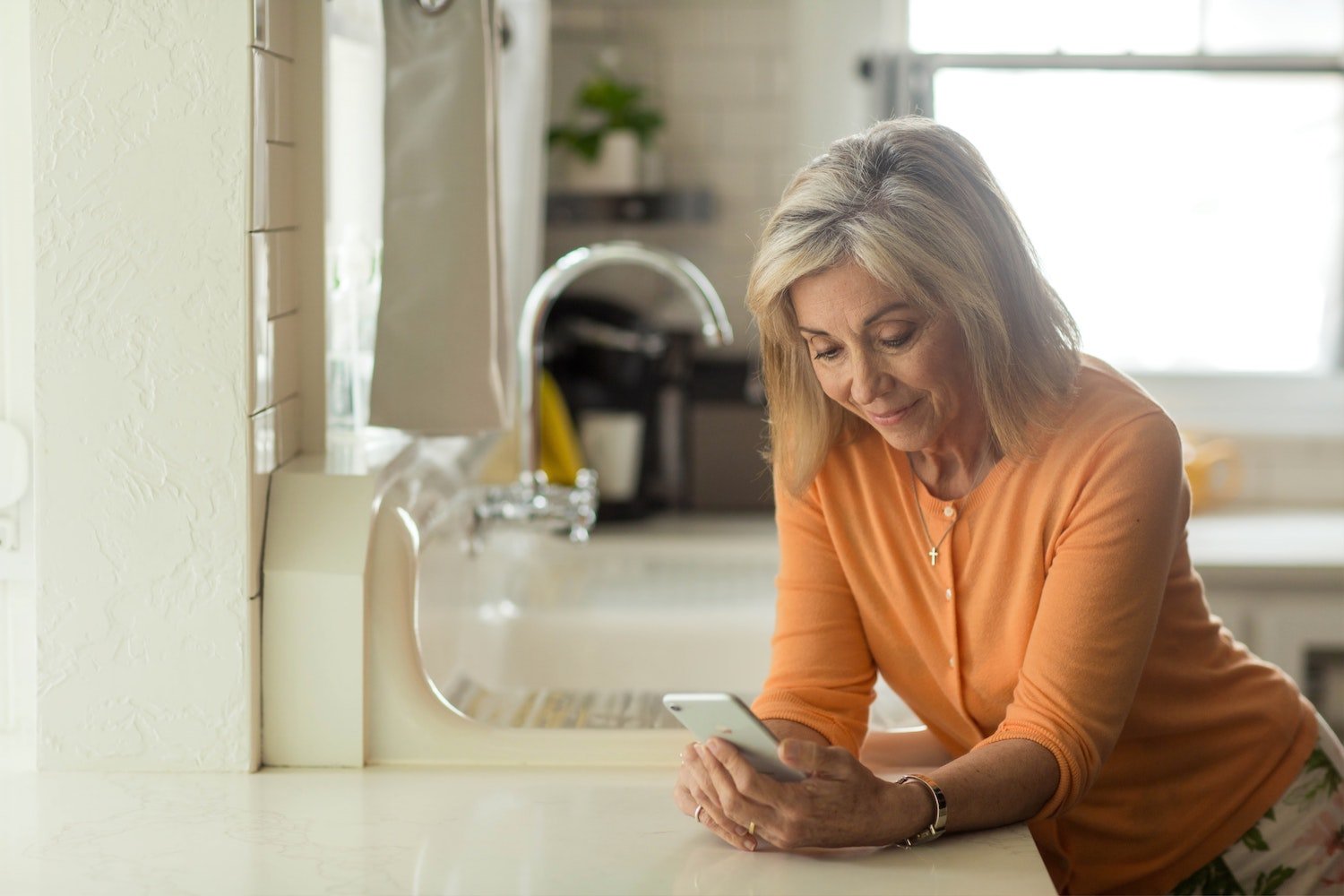
Telehealth and telemedicine solutions have been an indispensable part of the world’s fight against the COVID-19 virus. The ability of healthcare providers to consult with patients virtually eliminated many face-to-face visits and opportunities to spread the disease.
The population was able to maintain social distancing standards while still obtaining certain types of medical care that could be dispensed electronically.
Benefits of Telehealth Solutions
Table of Contents
In addition to the advantages telehealth offered to combat the pandemic, it promises to provide society with many other benefits. Following are some of the reasons telehealth solutions are gaining popularity among patients and providers.
- Reducing travel and waiting time – Telehealth can eliminate the cost and inconvenience associated with traveling and waiting for non-emergency healthcare visits.
- Providing enhanced care to remote communities – Patients living in rural communities requiring extensive travel for checkups and appointments are better served with telemedicine solutions. Especially in the case of follow-up visits, telehealth apps contribute to improved patient care and outcomes.
- Managing chronic conditions – Individuals with chronic conditions requiring extensive monitoring benefit from the care available with telehealth tools. Patients can easily contact providers to discuss ongoing treatment and receive updated care instructions related to their current status.
- Reducing overhead for providers – The cost of offering virtual appointments is much less than in-office visits, providing substantial savings for healthcare facilities. In addition, telehealth solutions reduce the number of no-show patients, minimizing the associated financial losses to the provider.
- Improving patient satisfaction – Reliable and accessible telehealth solutions improve patient satisfaction and confidence in their providers.
Telehealth will continue to grow in popularity for these and other related reasons as long as patient data can be kept secure.
Telehealth Security and Privacy Risks
The substantial benefits of telehealth come with increased risks to the security and privacy of sensitive patient data. The type of information contained in medical records and correspondence with providers presents an attractive target for hackers and cybercriminals. Citizens are understandably skeptical about how secure their sensitive information is when stored and processed electronically.
Data breaches and ransomware attacks occur virtually every day. By definition, all data breaches affect some kind of sensitive data. The special nature and sensitivity of medical information set it apart, making its security more important.
Concerns about sensitive medical information were first addressed in the U.S. by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA). HIPAA defines protected health information (PHI) and electronically protected health information (ePHI) as data that can be used to identify medical records with a specific patient. They list 18 identifiers that include things like the patient’s name, Social Security, email address, and phone number.
These data elements are required to be protected by healthcare providers and the business associates who process patient information and records. Failure to maintain the privacy and security of ePHI subjects the offending organization to financial penalties and can destroy the confidence of its customers.
Before the introduction of telehealth solutions, electronic patient data that fell under HIPAA guidelines was primarily protected by dedicated information technology (IT) professionals. As the role of telemedicine increases, so do the risks to ePHI. The convenience and personalized use of apps that process ePHI introduce a large and diverse attack platform.
Techniques to Minimize the Security Risks in Telemedicine
The risks to telehealth solutions are real and need to be addressed effectively for society to enjoy all of its potential benefits. Patients who are concerned about the security and privacy of their medical information will not be motivated to adopt telemedicine apps. Gaining their confidence in the security of telehealth products is essential to promoting their widespread use.
Therefore, maintaining the security and privacy of patient data is the most important characteristic of a viable telehealth solution. Let’s look at this issue from the perspectives of providers and patients.
Providers
Healthcare providers should incorporate the following methods and practices when employing any telemedicine application with their patients.
- Use HIPAA-compliant solutions – Strive to use HIPAA-compliant solutions when offering telehealth services. Some guidelines regarding security were temporarily waived to address the COVID-19 emergency. These requirements will eventually be enforced again, and HIPAA-compliant solutions should be put in place. This includes hosting systems with HIPAA-compliant providers and using apps that meet HIPAA standards.
- Data encryption – All ePHI should be encrypted when used in any telehealth application. This includes third-party and cloud solutions which should be obtained from reliable providers.
- Multi-factor authentication – Use multi-factor authentication to improve the security of sensitive data. Apps requiring multi-factor authentication provide additional layers of security and help minimize data breaches and successful cyberattacks.
- Limit network access – Prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information by practicing the principle of least privilege. Techniques like network segmentation should be implemented by providers or their business associates to limit the potential misuse of ePHI. Cloud telehealth solutions should use dedicated private networks to protect data transmission.
- Manage mobile device access – Employees’ personal mobile devices should not have access to sensitive apps, networks, or patient data. Ensure that company-owned devices with the appropriate level of security are used to access and process ePHI.
- Use a secure area for telehealth visits – Limit access to the area to healthcare professionals required for a patient’s care. Secure visual and audio access to the content of a telehealth session. Sign out of all apps when the session ends and limit information requests to those necessary to treat the patient. This should be automatically enforced.
- Keep patients informed – Organizations should keep their patients informed regarding the privacy and security measures that have been implemented to protect their data.
Patients
Patients also have roles and responsibilities regarding the protection of their sensitive health information.
- Stay informed – Request information from your provider regarding their privacy and security practices. Know when you should be expecting telehealth communication. Be cautious of unexpected or suspicious contact through voice or email that may indicate a scam. Contact your provider directly if you have concerns.
- Keep your device secure – Maintain security on the device used for telehealth visits so it cannot be used by unauthorized individuals to compromise your information.
- Ensure the session is secure – Ask your provider if the communication is protected and verify data transmission is encrypted.
- Choose a private location – Control who has access to conversations or video conferences with your healthcare provider. Consider using a room with a door if necessary.
- Watch the backdrop – Remember that whatever is behind you will be visible during video communication. Remove anything that you may not want to share with your provider.
- Keep your computer and devices updated – Manufacturers regularly provide updates and patches that improve security. You must apply these updates to protect your sensitive data.
- Avoid public WiFi – Try to conduct telehealth visits using a private network to improve your security.
Conclusion
Despite the potential risks to privacy and security, telehealth solutions are here to stay. The benefits to healthcare patients and providers are too great to ignore. It’s up to application developers and the organizations that implement their telemedicine solutions to take the necessary steps to ensure the security and privacy of ePHI.
Patients also need to understand their responsibility in protecting their sensitive information. With the proper safeguards, telehealth can provide a secure and flexible method of providing society with improved and flexible healthcare options.