In CSS, we’re given a tool to explicitly control the stacking order of HTML elements: z-index. Elements with a higher value will appear on top:
Because .first.box has a larger z-index than .second.box, it stacks in front. If we remove that z-index declaration, it falls to the back. The code above is editable—give it a shot!
Things aren’t always so simple, however. Sometimes, the larger z-index value doesn’t win.
Check out what’s going on here:
.tooltip has a much larger z-index than header! So why on earth is the header on top?
To unravel this mystery, we’ll need to learn about stacking contexts, an obscure-yet-fundamental CSS mechanism. In this article, we’ll explore what they are, how they work, and how we can use them to our advantage.
the full list on MDN.
This can lead to some surprising situations. Check out what’s happening here:
main doesn’t set a z-index anymore, but it uses will-change, a property that can create a stacking context all on its own.
In order for z-index to work, we need to set position to something like relative or absolute, right?
Not quite. Check out what’s happening here:
The second box is lifted above its siblings using z-index. There are no position declarations anywhere in the snippet, though!
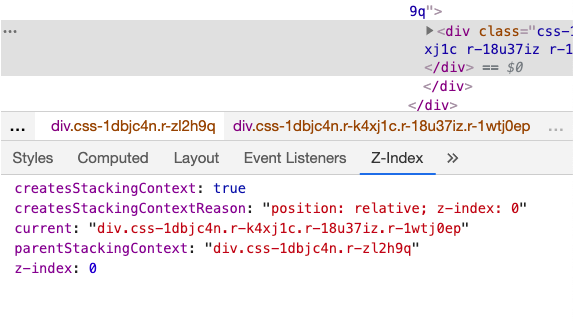
In order to understand what’s going on here, we need to learn about an iron-clad rule in CSS: only elements that create a stacking context can be given a z-index.
Remember the list we saw above? z-index will work in any of those situations. In this case, a stacking context is created by using z-index on a flex child (an element inside a container with display: flex).
In other words: it’s not that z-index only works with positioned elements. z-index works with any element that creates a stacking context. position: relative; z-index: 1 is one way to create a stacking context, but it’s not the only way.
Link to this heading
Hold on a minute…
There’s a Weird Thing here, and I think it’s worth pondering about for a minute or two.
In our Photoshop analogy, there is a clear distinction between groups and layers. All of the visual elements are layers, and groups can be conjured as structural helpers to contain them. They are distinct ideas.
On the web, however, the distinction is a bit less clear. Every element that uses z-index must also create a stacking context.
When we decide to give an element a z-index, our goal is typically to lift or lower that element above/below some other element in the parent stacking context. We aren’t intending to produce a stacking context on that element! But it’s important that we consider it.
When a stacking context is created, it “flattens” all of its descendants. Those children can still be rearranged internally, but we’ve essentially locked those children in.
Let’s take another look at the markup from earlier:
By default, HTML elements will be stacked according to their DOM order. Without any CSS interference, main will render on top of header.
We can lift header to the front by giving it a z-index, but not without flattening all of its children. This mechanism is what led to the bug we discussed earlier.
We shouldn’t think of z-index purely as a way to change an element’s order. We should also think of it as a way to form a group around that element’s children. z-index won’t work unless a group is formed.
Link to this heading
Airtight abstractions with “isolation”
One of my favourite CSS properties is also one of the most obscure. I’d like to introduce you to the isolation property, a hidden gem in the language.
Here’s how you’d use it:
When we apply this declaration to an element, it does precisely 1 thing: it creates a new stacking context.
With so many different ways to create a stacking context, why do we need another one? Well, with every other method, stacking contexts are created implicitly, as the result of some other change. isolation creates a stacking context in the purest way possible:
-
No need to prescribe a z-index value
-
Can be used on statically-positioned elements
-
Doesn’t affect the child’s rendering in any way
This is incredibly useful, since it lets us “seal off” an element’s children.
Let’s look at an example. Recently, I built this neat envelope component. Hover or focus to see it open:
It consists of several layers:
I packaged this effect up in a React component, <Envelope>. It looks something like this (inline styles used for brevity):
(If you’re wondering why Flap has a dynamic z-index, it’s because it needs to shift behind the letter when the envelope is open.)
A good React component is sealed off from its environment, like a spacesuit. This spacesuit, however, has sprung a leak. Check out what happens when I use it near a <header> with z-index: 3:
Our <Envelope> component wraps the 4 layers in a div, but it doesn’t create a stacking context. As a result, those layers can become “intertwined” with other components, like the world’s most boring game of Twister.
By using isolation: isolate on the top-level element within <Envelope>, we guarantee that it’ll be positioned as a group:
Why not create a stacking context the old-fashioned way, with position: relative; z-index: 1? Well, React components are meant to be reusable; is 1 really the right z-index value for this component in all circumstances? The beauty of isolation is that it keeps our components unopinionated and flexible.
More and more, I’m starting to believe that z-index is an escape hatch, similar to !important. This is one trick that allows us to control stacking order without pulling the big red z-index lever.
I’m working on a follow-up tutorial where we look at some other tricks to keep z-index inflation down. Watch this space!
very good browser support: it works in every browser except Internet Explorer.
If I needed to support Internet Explorer, I would consider using transform: translate(0px); instead. I haven’t tested it, but I believe it would achieve the same result: creating a stacking context without any meaningful side-effect.