In 2023, the world has felt like it was balanced on a precipice. A United States presidential election looms, with a resurgent candidate that threatens to bring with him all the chaos of 2016 and 2020. Artificial intelligence developed so quickly that it seemed to have suddenly sprung into being, heralding vast societal promise and disruption just around the bend of its exponential curve. And the world’s richest man continued to use his power to push for a more reckless tech world, from free-for-all social media and oversold assisted-driving features to AI with a “rebellious streak.”
In the midst of that uncertainty, a new war between Israel and Hamas added more atrocities alongside the slow-burning horrors of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. These wars have echoed across the internet in propaganda, hate speech, and cyberattacks that triggered widespread real-world effects. Chinese state-sponsored hackers, meanwhile, sowed the seeds for a future cyberwar, and ransomware gangs resurged. It was a banner year for chaos, present and impending, and all reflected in the digital mirror.
Each year, WIRED assembles a list of the most dangerous people, groups, and organizations on the internet—both those who intentionally endanger innocent people and those whose actions, regardless of their intent, destabilize the world as we know it in myriad ways. Here, in no particular order, are our picks for 2023.
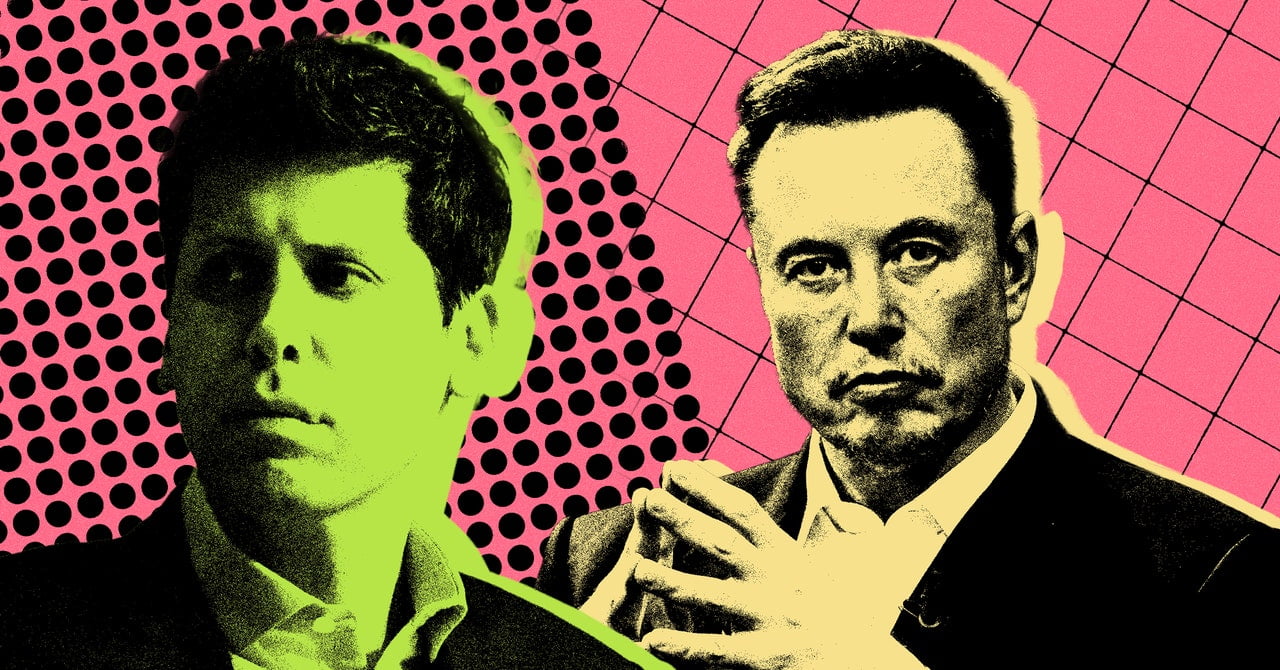
A year ago, it might have still been fair to regard Elon Musk as a brilliant technologist with occasional destructive, trollish tendencies. In 2023, those tendencies seemed to take over his public identity. Twitter, now renamed X thanks to Musk’s branding whims, this year invited back conspiracy theorists like Alex Jones and even amplified one account’s antisemitic statements. When advertisers complained, Musk managed in a single conversation to both apologize for that blunder and tell them, “Go fuck yourself.”
Before that, in July, Musk had said that his social media platform’s ad revenue had fallen by half—all of which calls into question whether this once-central platform for online conversation will survive Musk’s reign, and in what form.
In the midst of that meltdown, Musk’s new startup xAI released Grok, an AI chatbot Musk celebrated for having fewer guardrails than OpenAI’s ChatGPT. Musk faces calls for an SEC investigation for his comments about how monkeys died in experiments carried out by his brain implant startup Neuralink. And in mid-December, Tesla recalled nearly every model of its vehicles sold in the US to fix an Autopilot feature. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration found that Tesla’s safety measures for assuring that drivers paying attention—which many no doubt were not, perhaps thanks in part to Musk’s own descriptions of the assisted-driving feature—were inadequate.
Five years ago, WIRED put Musk’s face on the cover with a story that described his Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde personality. These days, it’s becoming clearer which side of that split personality dominates.
In 2023, ransomware resurged. According to cryptocurrency firm Chainalysis, it appears to be on track to be the second-worst year on record in terms of total extortion payments collected by the ransomware industry’s coercive gangs of hackers. But perhaps no group did more damage this year than the people behind the Cl0p malware.
In May, the Cl0p gang began exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in the MOVEit file transfer software and used it to carry out a shocking spree of intrusions across more than 2,000 organizations, according to ransomware-focused security firm Emsisoft. A single victim, medical firm Maximus, lost control of the data of at least 8 million people in the breach. The hackers stole data from the state government of Maine on another 1.3 million. In total, at least 62 million people were affected, and Cl0p’s hackers remain at large.
If Cl0p were the most ruthless ransomware hackers of the year, Alphv, also known as Black Cat, were certainly in close contention. The group, which has ties to the hackers who carried out the 2021 cyberattack on the Colonial Pipeline, gained a new level of notoriety in September when it targeted MGM Resorts International, shutting down computer systems across the hotel and casino chain and ultimately doing $100 million in damage, by MGM’s estimate. More broadly, the FBI says that Alphv has compromised over a thousand organizations and extracted more than $300 million in ransoms.
In mid-December, the FBI announced that it had seized the dark-web site where Alphv publishes its victims’ stolen data. Hours later, the site reappeared, and Alphv defiantly announced it had “unseized” it and would no longer abide by a rule not to target critical infrastructure systems. The site was soon taken down again. But given that no members of the group have been arrested or even indicted in absentia, its chaos will likely continue.
No event of 2023 has shaken geopolitics as suddenly and shockingly as Hamas’ atrocities against civilians in Southern Israel on October 7. The attacks, in which Hamas militants killed 1,200 people and took hundreds of hostages, immediately triggered a war that threatens to destabilize the region. It has also shaken the tech world, where it has raised questions about the digital technologies that have enabled Hamas, from the millions of dollars the group raised via cryptocurrency to its channels on Telegram, where it distributes propaganda and videos of its violence. When ISIS came to prominence in 2014, it forced every technology platform in the world to question whether and how it enabled extremist violence. Now, a decade later, a new round of horrific bloodletting shows how that reckoning continues.
Despite sanctions, indictments, and even a $10 million bounty, Russia’s team of hyper-aggressive military intelligence hackers known as Sandworm are still out there—and still active. As Russia’s invasion of Ukraine grinds toward its third brutal year, in fact, they appear to have turned their focus to that conflict.
This year, Sandworm was revealed to have carried out a third blackout cyberattack against a Ukrainian electric utility, this time in the midst of a Russian air strike hitting the same city. It later penetrated Ukrainian military communications in a more traditional espionage-focused effort to gain an advantage during Ukraine’s counteroffensive. And evidence points to Sandworm’s responsibility for a cyberattack just this month that hit the telecom Kyivstar, taking out internet and mobile communications for millions amid another series of strikes. The group, in other words, continues to earn its reputation as the Kremlin’s most dangerous hackers.
For years, the cybersecurity community has asked itself who might be the “Sandworm of China.” This year provided perhaps the closest thing yet to an answer. The hacker group dubbed Volt Typhoon by Microsoft was revealed in May to have planted malware in power grid networks across the continental US and Guam, in some cases with an apparent eye toward controlling the flow of electricity to US military bases. More recently, The Washington Post revealed that Volt Typhoon’s targets have extended to other kinds of critical infrastructure too, from an oil and gas pipeline to a major West Coast port and a Hawaiian water utility.
While the intentions of the group and its overseers are still far from clear, cybersecurity and geopolitical analysts increasingly see it as laying the groundwork to disrupt key US systems in the event of a crisis—such as China invading Taiwan.
Last year, for the first time since 2015, Donald Trump was not included on this list. Hope you enjoyed the break!
Less than 11 months out from the 2024 US presidential election, Trump leads Republican primary polls by a wide margin. He has used his rekindled relevance to launch disturbing attacks on his perceived enemies, largely from his own right-wing-dominated Truth Social platform.
In posts there, he has vowed, if elected, to launch federal investigations into media companies and journalists that criticize him and to prosecute President Biden. He has ranted about the wife of one of the judges overseeing a civil trial against him for fraud charges and blamed his political opponents for the criminal charges he faces for allegations of election interference and improper handling of classified information. And he has continued to tout his discredited claims of winning the 2020 election, which the US Department of Justice says fueled the January 6, 2021, storming of the US Capitol.
More to the point, all of this may be finding a receptive audience among Trump’s base. That means it could help usher in another presidency of the kind that pulled the US out of the Paris Agreement on climate change, instituted a “Muslim ban” and family separation border policy, dismantled pandemic protections, and denied the seriousness of Covid-19 as hundreds of thousands of American died. Here we go again.
Since October 7, Israel’s military has responded to Hamas’ invasion of Israel with attacks that have killed at least 20,000 Palestinians—largely women and children—displaced nearly 2 million of Gaza’s inhabitants, and cut off the flow of food, water, and medicine to the region. It has also at times taken out Gaza’s telecommunications and internet to leave it in a near-total information blackout, even as it claims it’s using those communication tools to warn civilians about its impending attacks on their homes.
In the midst of all of this, Israel’s propaganda machine has been working to shape the public narrative about its military operations, from promoted tweets by the IDF in support of its campaign in Gaza appearing on X to Israeli accounts going so far as to claim that Palestinian deaths have been staged with dolls made to look like dead infants. All of that has played a role in silencing global criticism of the IDF’s actions even as the death toll from its war against Hamas stretches an order of magnitude beyond that of Hamas’ October 7 atrocities.
Running the company that’s arguably leading the race to develop the most disruptive technology ever imagined is enough to qualify anyone as one of the most dangerous people to exist—not just this year but in human history. Setting that small point aside, Altman might seem at a glance like the most benign personality imaginable to serve as OpenAI’s CEO. He has chosen, surprisingly, to take no equity stake in the company. He argues for more government regulation of AI in interviews and congressional hearings. He genuinely seems to believe in a flourishing future for humanity in a post-singularity world.
But November’s brief and dramatic power struggle within OpenAI exposed a less reassuring side to the company’s leader and the newly consolidated circle of power that surrounds him. Altman had argued in the past that the strange structure of OpenAI, with a nonprofit overseeing a for-profit company, offered a form of self-restraint that would keep the company’s technological ambitions on a safety-conscious leash. But when Altman was fired by OpenAI’s board and almost immediately wrested back control of the company while ousting several board members—including two ethics-focused effective altruists—the leash snapped. OpenAI, in this new era, is now firmly under the control of one man and his executive team, as well as Microsoft, his $2.8 trillion corporate ally and investor.
So let’s hope his plan for the future of this world-flipping technology is a good one. Either way, it will be very hard to stop him.
The group that calls itself Predatory Sparrow, a translation from the Persian Gonjeshke Darande, is hardly a household name in the cybersecurity world. But it raised alarms in 2022 when it carried out a cyberattack on several Iranian companies, including a steel mill where it claimed—and posted video to show—that it had somehow started a fire in the facility. The group, which styles itself as hacktivists but which the Iranian government has claimed is linked to the Israeli state, also leaked a collection of documents stolen in those breaches that the hackers said revealed the companies’ connections to the Iran Revolutionary Guard Corps.
Now, in the wake of the Israel-Hamas war, and as Houthi rebels fire Iranian missiles at Israel, Predatory Sparrow has carried out a second major cyberattack against Iran, this time reportedly disabling as many as 70 percent of gas stations across the country. This will be one to watch.
Title: An Insight into the Internet’s Most Perilous Individuals in 2023
Introduction:
As technology continues to advance, the internet has become an integral part of our lives, connecting people from all corners of the world. However, with this connectivity comes a darker side. The internet is also home to some of the most perilous individuals, who exploit its anonymity and reach to cause harm. In this article, we will delve into the world of the internet’s most dangerous individuals in 2023, shedding light on their activities and the measures being taken to combat them.
1. Cybercriminals:
Cybercriminals are at the forefront of online threats, constantly evolving their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in technology and human behavior. These individuals engage in various criminal activities, including hacking, identity theft, financial fraud, and spreading malware. They target individuals, businesses, and even governments, causing significant financial losses and compromising sensitive information.
To combat cybercriminals, governments and organizations are investing heavily in cybersecurity measures. This includes implementing robust encryption protocols, raising awareness about online threats, and developing advanced artificial intelligence systems to detect and prevent cyberattacks.
2. Online Extremists:
The rise of social media platforms has provided a breeding ground for online extremists. These individuals use the internet to spread hate speech, incite violence, recruit terrorists, and promote extremist ideologies. Their activities pose a significant threat to global security and social harmony.
Governments and tech companies are working together to counter online extremism. They employ advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify and remove extremist content promptly. Additionally, initiatives are being taken to promote digital literacy and critical thinking skills to help individuals recognize and reject extremist ideologies.
3. Online Predators:
The internet has unfortunately become a hunting ground for online predators who target vulnerable individuals, particularly children. These individuals engage in grooming, exploitation, and distribution of child pornography. They often operate in hidden corners of the internet, making it challenging for law enforcement agencies to track them down.
To combat online predators, governments are strengthening legislation and international cooperation to enhance the investigation and prosecution of such criminals. Additionally, organizations and individuals are actively involved in educating children and parents about online safety, emphasizing the importance of privacy settings, and promoting responsible internet usage.
4. State-Sponsored Hackers:
State-sponsored hackers pose a significant threat to national security and global stability. These individuals, often backed by governments, engage in cyber espionage, intellectual property theft, and disruption of critical infrastructure. Their activities can have far-reaching consequences, impacting economies, political systems, and even public safety.
Governments are investing heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect their critical infrastructure from state-sponsored hackers. This includes developing advanced threat intelligence capabilities, conducting regular security audits, and collaborating with international partners to share information and coordinate responses.
Conclusion:
The internet’s most perilous individuals in 2023 continue to exploit the vast opportunities provided by technology. However, governments, organizations, and individuals are not standing idly by. They are actively working together to develop robust cybersecurity measures, raise awareness about online threats, and promote responsible internet usage. By staying vigilant and taking necessary precautions, we can collectively mitigate the risks posed by these dangerous individuals and ensure a safer online environment for all.